Concepts¶
Architecture¶
Koala consists of multiple separate processes (red) and middleware components (blue).
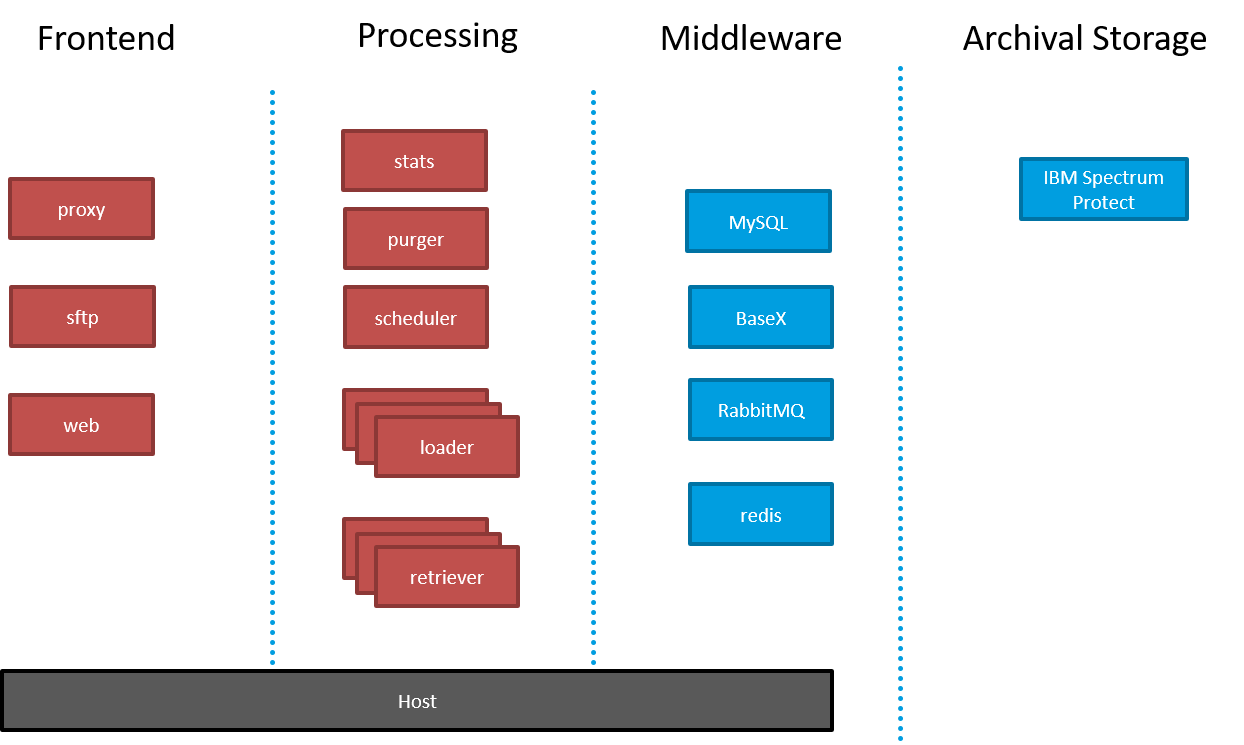
Middleware¶
Data Management (DB)¶
Primary Datastore. Contains Asset metadata, information regarding ingest and retrieval requests as well as known filetypes, schemas and user information. Currently supported is mysql
Message Queue (MQ)¶
The message queue is used to asynchronously route ingest and retrieval requests to loader/retriever applications. Currently supported is RabbitMQ
Archival Storage¶
Physically stores the assets. Multiple implementations of an Archival Storage client are available, for example TSM, filesystem.
Cache¶
Stores heartbeat informations about the running applications which is shown on the web application. Retrieves and caches statistics about the archived packages from the main database. Currently supported is redis
Applications¶
Scheduler¶
Monitors the upload directory for new SIPs and publishes the data for further processing to the message queue. Only one scheduler must be running at the same time.
Loader¶
Multiple Loaders can be started simultaneously which then connects to the message broker and processes the SIPs
concurrently.
Processing includes among others the following steps:
- unzipping
- validating files and metadata
- calculating checksums
- storing metadata in DB and assets in Archival Storage.
The status of the ingest process is continuously updated and can be monitored through the Web UI or API.
Proxy¶
A reverse proxy for SSL offloading and serving of static content.
Web¶
Provides a http api for third party applications and a web ui for admin operations.
Retriever¶
Multiple Retriever can be started simultaneously which then connects to the message broker and processes retrieval requests from clients. AIPs are fetched from the Archival Storage system, afterwards converted to a DIP and saved in the http accessable downloadrea. The status of the retrieval process is continuously updated and can be monitored through the Web application.
Purger¶
Monitors the downloadarea filesystem size and removes old packages once the highwatermark is reached.
Statistics¶
Queries the main database, calculates statistics and saves the information in the cache.
Processes¶
Ingest¶
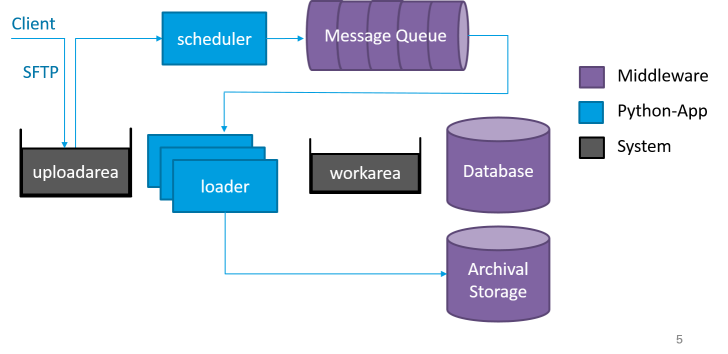
The ingest process is modeled as a state machine with done/error/fatal end states. As soon as the client gets a "done" ticket by the web application, the AIP is saved on stable storage (archival storage) and every participating system has the required data e.g. mdqi, data management. Every ingest of a SIP is also a "transaction" which means that a failing step leads to a recovery/rollback operation. The recovery is done by the loader error state or in case the operation was fatal by the purger application. During the recovery procedure the purger locks the corresponding workarea and blocks the loader application from starting.
Retrieve¶
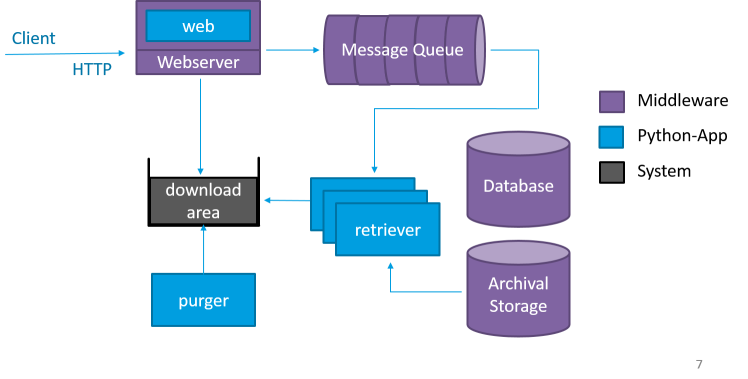
When the client requests a specific package, a retriever application saves the data to the http accessible downloadarea. The DIPs remain accessible until a configured threshold is reached. Typically 70% downloadarea usage. Then DIPs are being removed from oldest to newest by the purger application.